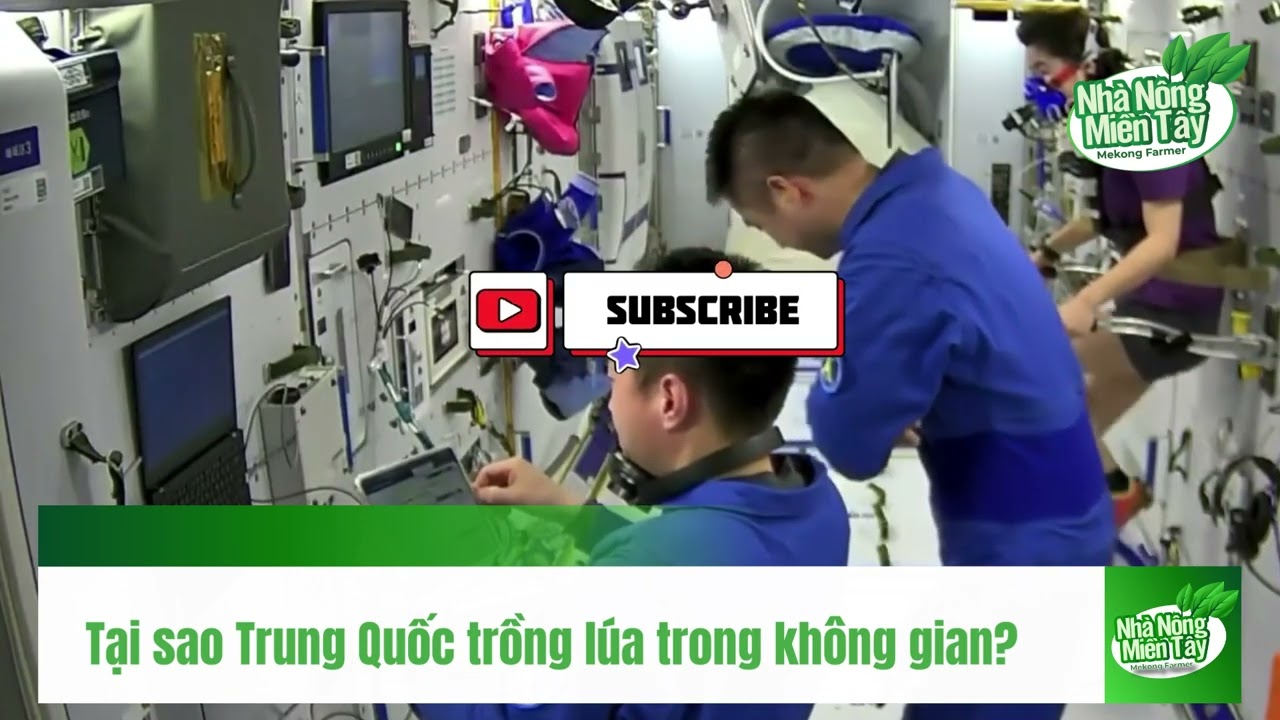
Why is China growing rice in space? Chinese astronauts have recently begun growing rice as part of an experiment to recreate a full life cycle in space for the first time. The Tiangong space station has more tenants than originally planned, and the rice plants, the first to be brought aboard to recreate a full life cycle in space, have adapted perfectly to extraterrestrial life and are thriving. These experiments will be key to feeding crews on future long-duration space missions, and will change astronauts’ diets a bit beyond canned and preheated food. Food for Mars Zheng Huiqiong, an expert from the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, explained that the rice shoots have reached “30 centimeters in height,” adding that the goal is to “investigate how microgravity can affect the flowering time of plants at the molecular level.” and if microgravity can be used to control the processes.” Reaching Mars on a manned mission like the one we have now would leave the crew without food, and they wouldn’t be able to store enough food on board to complete the trip. That’s why it’s important that the rice plants adapt and grow to be self-sufficient in space. Agricultural Space Lab The experiment is being carried out inside the Wentian Space Lab, which docked to the Tianhe core module of the Tiangong station on July 24 and began cultivation five days later. The astronauts will continue to analyze the plants’ growth, and if they complete the full life cycle, they will bring the seeds back to Earth for further study. The Tiangong station currently under construction, dubbed “Palace in the Sky,” will weigh about 70 tons upon completion and is expected to operate for about 15 years in an orbit about 400 kilometers (250 miles) above Earth’s surface. #farmland #farmspace #china #farmfarmers #farmerswestern
source